Did you know that you can navigate the posts by swiping left and right?
Intro to Artificial Neural Network
23 Apr 2018
. category:
tech
.
Comments
#tutorial
Neural network is a model that is inspired by how neurons in the human brain work. Each neuron in the human brain is interconnected and information flows from each neuron. The picture below is a neuron illustration with its mathematical model.
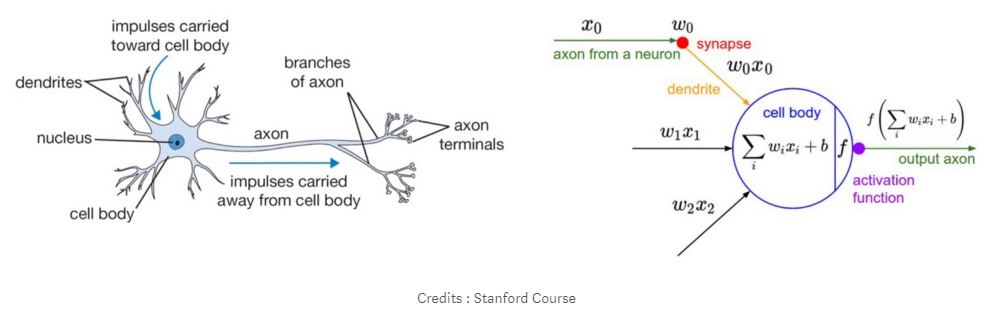
Each neuron receives input and performs a dot operation with a weight, adds it (weighted sum) and adds bias. The result of this operation will be the parameter of the activation function that will be the output of the neuron.
Activation Function
As the name implies, the activation function functions to determine whether the neuron should be “active” or not based on the weighted sum of the input. In general there are 2 types of activation function, Linear and Non-Linear Activation function.
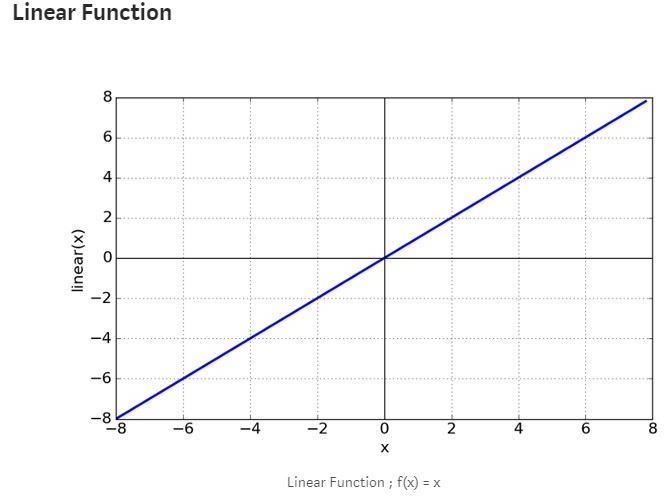
It can be said that the “default” activation function of a neuron is Linear. If a neuron uses a linear function, then the output of the neuron is the weighted sum of the input + bias.
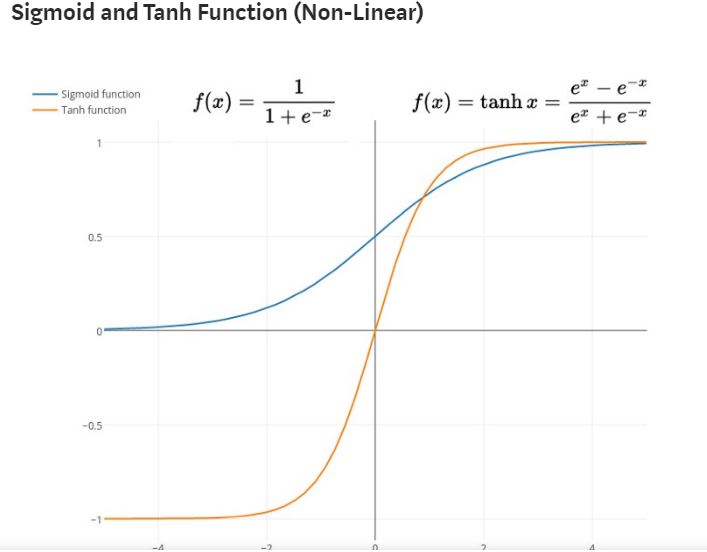
Sigmoid function has a range between 0 to 1 while the range from Tanh is -1 to 1. Both of these functions are usually used for classification of 2 classes or groups of data. But there are disadvantages of these two functions.
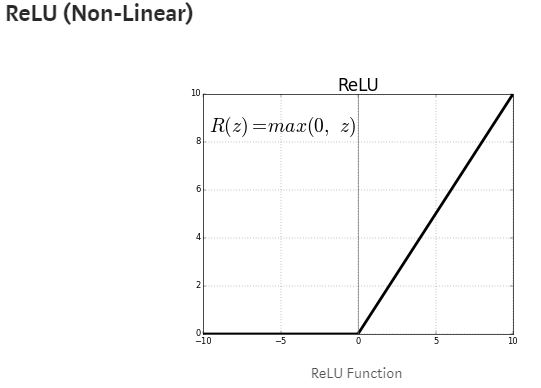
Basically ReLU performs a “treshold” from 0 to infinity. ReLU can also cover the weaknesses possessed by Sigmoid and Tanh
Neural Network Architectures
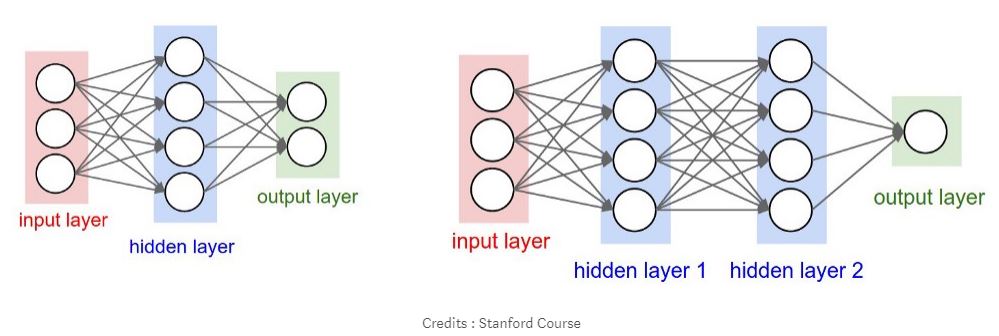
The above architecture is commonly referred to as Multi Layer Perceptron (MLP) or Fully-Connected Layer. The first architecture has 3 neurons in the Input Layer and 2 Output Layer nodes. Among Inputs and Outputs, there is 1 Hidden Layer with 4 neurons. While the Weight and Activation function specifications are as follows:
Weight and Bias
Each neuron in the MLP is interconnected which is marked by arrows in the image above. Each connection has a weight that will be the value of each weight will vary. Hidden layer and output layer have additional “input” commonly called bias (Not mentioned in the picture above). So in the first architecture there are 3x4 weight + 4 bias and 4x2 weight + 2 bias. Total is 26 parameters that the training process will undergo changes to get the best result. While on the second architecture there are 41 parameters.
Activation Function
Neurons in the input layer do not have activation function, while neurons in hidden layer and output layer have activation function which sometimes differ depending on data or problem that we have.
Training a Neural Network
In Supervised Learning using Neural Network, in general, Learning consists of 2 stages, namely training and evaluation. But sometimes there is an additional stage of testing, but its not mandatory. At the training stage each weight and bias on each neuron will be updated continuously until the output produced in accordance with expectations. At each iteration will be a process evaluation which is usually used to determine when to stop the training process (stopping point) The training process consists of 2 stages:
- Forward Pass
- Backward Pass
Forward Pass
Forward pass or commonly called forward propagation is the process by which we carry data on the input through each neuron in the hidden layer to the output layer which will be calculated the error
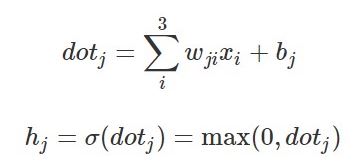
The above equation is an example of a forward pass on the first architecture (see the architecture picture above) that uses ReLU as an activation function. Where i is the node on the input layer (3 input nodes), j is the node on the hidden layer whereas h is the output of the node on the hidden layer.
Backward Pass
The error we get on the forward pass will be used to update each weight and bias with a certain learning rate. Both of the above process will be done repeatedly until we get the value of weight and bias that can give the error value as small as possible at the output layer (at the time of forward pass)
